Introduction to Marine Insurance
Marine insurance is a type of insurance that provides financial protection for ships, cargo, and goods transported over water. It helps cover the risk of damage, loss, or theft during transit by sea, river, or inland waterways. In simple terms, if anything happens to a ship or the goods on it, marine insurance helps recover the losses. Marine insurance is one of the oldest types of insurance in the world, with roots going back to the early days of trade and exploration.
Why Marine Insurance is Important
Marine transportation is risky. Ships travel long distances through oceans and face natural dangers such as storms, accidents, and piracy. Businesses that import or export goods must protect themselves from these risks.
Here’s why marine insurance matters:
- Protects against loss or damage to goods during transit
- Minimizes financial risks for businesses and shipowners
- Ensures smooth trade operations
- Builds trust between buyers and sellers
Without marine insurance, even one accident could cause huge losses to companies.
Scope of Marine Insurance
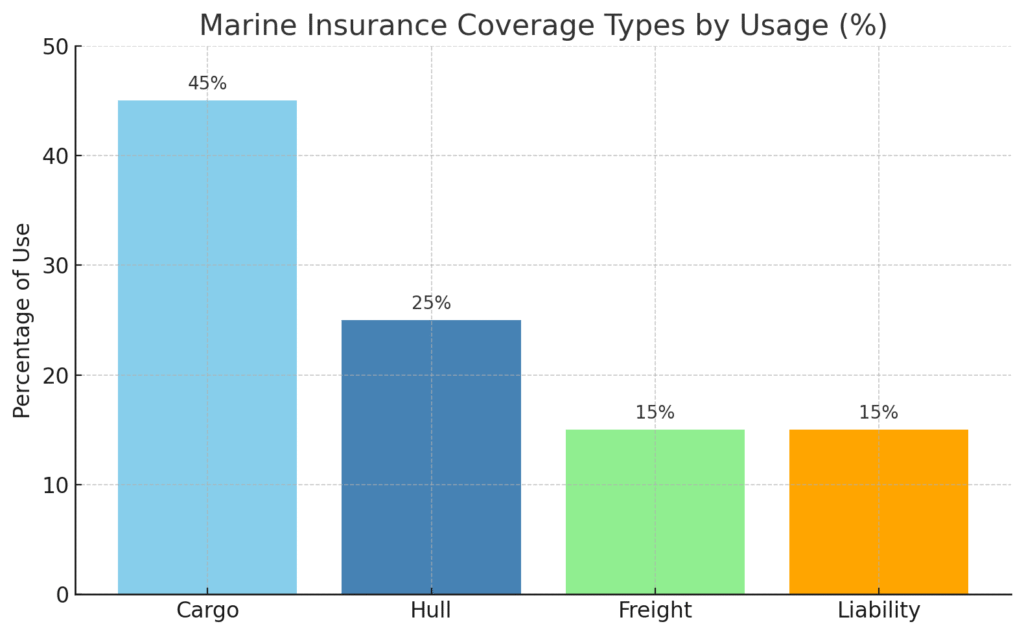
The scope of marine insurance means what this insurance policy covers. Marine insurance can cover various parts of the shipping process, depending on the type of policy chosen.
3.1 Cargo Insurance
Cargo insurance covers the goods or cargo transported by ship. If the goods are damaged, lost, or stolen during the journey, the insurance company pays for the loss.
Example: A company sends electronics from India to the UK. During the journey, water leaks into the container and damages the products. Cargo insurance helps recover the cost.
3.2 Hull Insurance
Hull insurance covers the physical body of the ship—its structure, engine, and machinery. If the ship is damaged in an accident, hull insurance pays for repairs or replacement.
Example: A ship collides with another vessel and gets a crack in the hull. Hull insurance helps pay for the repairs.
| Coverage Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Cargo Insurance | Covers goods during sea transport against loss, damage, or theft. |
| Hull Insurance | Protects the ship’s body, machinery, and equipment. |
| Freight Insurance | Covers the shipping charges if cargo is lost or damaged. |
| Liability Insurance | Covers legal liabilities for damages to third parties or the environment. |
3.3 Freight Insurance
Freight insurance protects the freight charges (the money paid to ship goods). If the cargo does not reach its destination safely, and the shipping company cannot collect its charges, freight insurance covers the loss.
Example: Goods are destroyed mid-way due to fire, and the shipping company cannot collect fees from the customer. Freight insurance helps recover the lost payment.
3.4 Liability Insurance
Liability insurance covers legal responsibility if the ship causes damage to other ships, ports, or people. It also includes pollution damage and other third-party claims.
Example: A ship spills oil into the ocean, harming marine life and nearby coastal areas. The shipping company is legally responsible. Liability insurance pays for clean-up and fines.
Types of Risks Covered
Marine insurance policies cover various kinds of risks, such as:
- Natural hazards like storms, tsunamis, and cyclones
- Man-made risks such as fire, collision, theft, and piracy
- Loading and unloading damage
- Jettison (throwing cargo overboard to save the ship)
- War risks and strikes (if specifically added to the policy)
However, some policies may exclude certain risks unless additional cover is purchased. Always read the policy carefully.
Who Should Buy Marine Insurance?
Marine insurance is important for:
- Exporters and Importers: To protect goods being sent or received
- Shipping Companies: To cover their vessels and crew
- Freight Forwarders and Logistics Providers: To reduce financial exposure
- E-commerce Businesses: Especially those that send goods overseas
- Boat and Yacht Owners: For personal or commercial vessels
In many cases, marine insurance is required by law or as a condition of trade contracts.
Real-Life Examples
Example 1 – Cargo Loss: A textile company sends garments from Mumbai to Dubai. Midway, a fire breaks out on the ship, damaging all the cargo. Cargo insurance covers the cost of lost goods.
Example 2 – Collision Damage: A ship carrying machinery crashes into another due to poor visibility. Hull insurance pays for the repairs, while liability insurance handles the compensation for the other party.
Example 3 – Delayed Freight Payment: Due to a customs issue, the cargo is stuck at port and rejected by the buyer. Freight insurance helps recover the shipping company’s payment.
Final Thought
The scope of marine insurance is broad and essential for anyone involved in sea transport. From covering cargo and ships to protecting against legal claims, marine insurance plays a crucial role in global trade.
FAQ’s
What is the Scope of Marine Insurance?
The scope of marine insurance refers to the range of protections and risks that a marine insurance policy covers during the transportation of goods or people over water. It outlines what can be insured, who can be insured, and under what circumstances the insurer will provide compensation.
What is a marine insurance policy in simple words?
A marine insurance policy is a contract that protects you from losing money if your ship or goods are damaged, lost, or stolen while being transported over water.
What is the salary of a marine insurance specialist?
The salary of a marine insurance specialist depends on experience, location, and company. On average:
- In India, the salary ranges from ₹4 lakh to ₹10 lakh per year.
- In the USA, it typically ranges from $50,000 to $100,000 per year.
Experienced professionals or those working in large firms can earn even more.
What are the principles of marine insurance?
The principles of marine insurance are basic rules that guide how marine insurance works. Here are the main ones in simple words:
- Utmost Good Faith – Both the insurer and the insured must share all important information honestly.
- Insurable Interest – You must have a financial interest in the ship or goods you’re insuring.
- Indemnity – Insurance will cover your actual loss, not help you make a profit.
- Contribution – If you have more than one policy, all insurers will share the loss fairly.
- Subrogation – After paying your claim, the insurer can recover the loss from a third party (if someone else was responsible).
- Proximate Cause – The insurance covers only if the main reason (cause) of the loss is included in the policy.
These principles help keep marine insurance fair and effective for everyone.
What is the nature and scope of marine insurance?
Nature and Scope of Marine Insurance:
- Nature: Marine insurance is a contract that protects ships, cargo, and related interests against loss or damage during transportation over water. It is based on trust, legal rules, and financial protection against maritime risks.
- Scope: The scope of marine insurance includes coverage for:
- Cargo (goods being shipped)
- Hull (the ship or vessel)
- Freight (the cost of transporting goods)
- Liability (legal claims if the ship causes damage)
It protects against risks like storms, fire, theft, sinking, and collisions. It is essential for businesses involved in shipping, importing, or exporting goods.




